publications
publications in reversed chronological order
2025
-
 Exploring Situated Stabilities of a Rhythm Generation System Through Variational Cross-ExaminationBłażej Kotowski, Nicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, and 2 more authorsSep 2025
Exploring Situated Stabilities of a Rhythm Generation System Through Variational Cross-ExaminationBłażej Kotowski, Nicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, and 2 more authorsSep 2025This paper investigates GrooveTransformer, a real-time rhythm generation system, through the postphenomenological framework of Variational Cross-Examination (VCE). By reflecting on its deployment across three distinct artistic contexts, we identify three stabilities: an autonomous drum accompaniment generator, a rhythmic control voltage sequencer in Eurorack format, and a rhythm driver for a harmonic accompaniment system. The versatility of its applications was not an explicit goal from the outset of the project. Thus, we ask: how did this multistability emerge? Through VCE, we identify three key contributors to its emergence: the affordances of system invariants, the interdisciplinary collaboration, and the situated nature of its development. We conclude by reflecting on the viability of VCE as a descriptive and analytical method for Digital Musical Instrument (DMI) design, emphasizing its value in uncovering how technologies mediate, co-shape, and are co-shaped by users and contexts.
-
 Learning Microrhythm in Uruguayan Candombe using TransformersAnmol Mishra, Satyajeet Prabhu, Behzad Haki, and 1 more authorJun 2025
Learning Microrhythm in Uruguayan Candombe using TransformersAnmol Mishra, Satyajeet Prabhu, Behzad Haki, and 1 more authorJun 2025Musicians rely on nuanced microrhythm, slight variations in timing, dynamics, and other aspects, to create an expressive rhythmic feel in music performance. Electronic music production often attempts to replicate these qualities through algorithmic manipulations to achieve similar effects. In this work, we address the generation of microrhythm using a method that learns microtiming and dynamics from onset timing and strength annotations of drum performances. We frame microrhythm learning as a sequence modeling task, leveraging a Transformer-based model. Our focus is on Uruguayan candombe drumming, where we explore its rhythmic patterns at both the beat and rhythmic cycle levels. To evaluate the model’s effectiveness in replicating the original microrhythm, we compare the mean, standard deviation, and histogram intersection of timing deviations and dynamics values at each subdivision for the original and the generated data. The model is deployed as a VST enabling artists to incorporate candombe grooves into drum scores. With this work, we aim to bridge the gap between algorithmic rhythm creation and the expressive qualities of live performance, striving to produce music with the authentic grooves of various Latin American genres.
-
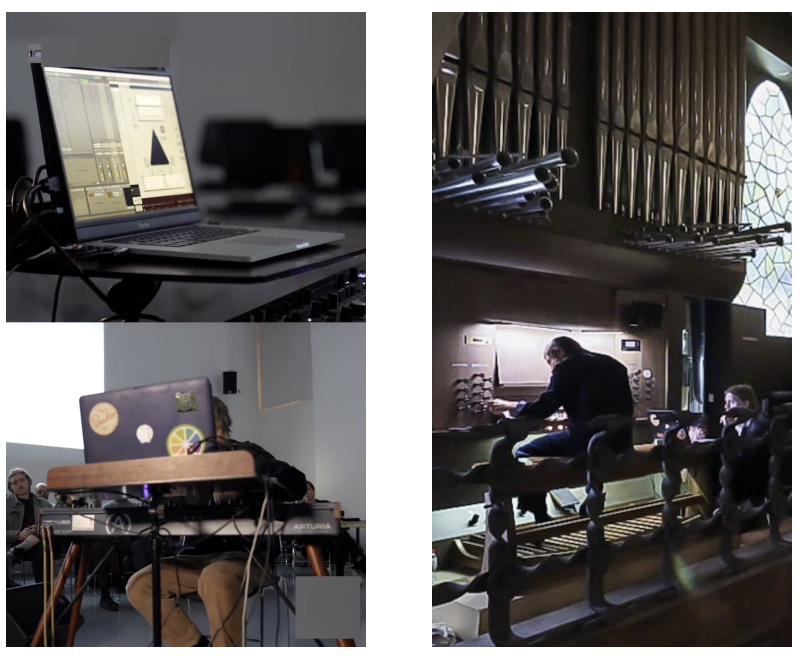
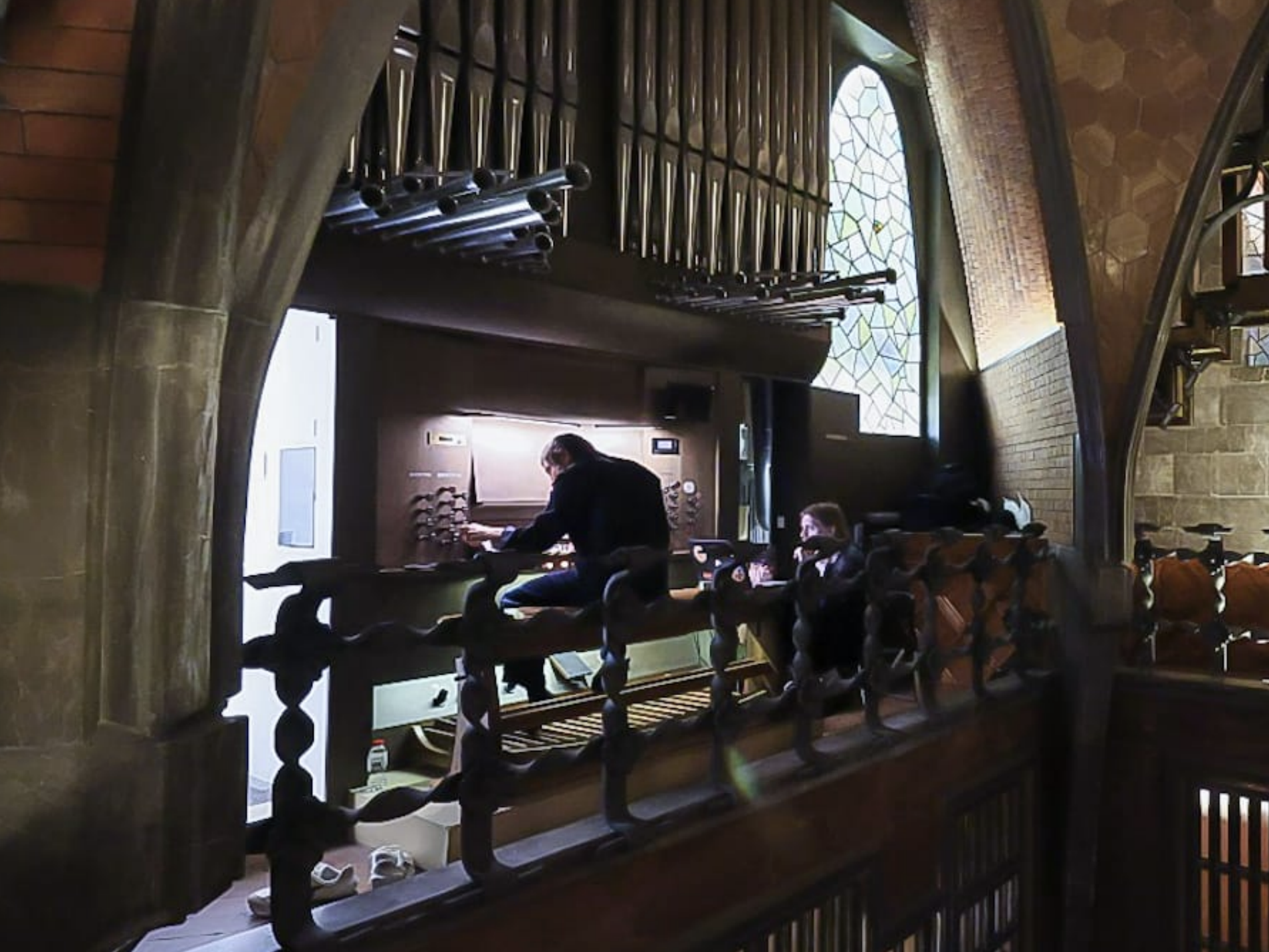 Repurposing a Rhythm Accompaniment System for Pipe Organ PerformanceNicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, and Sergi JordàJun 2025
Repurposing a Rhythm Accompaniment System for Pipe Organ PerformanceNicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, and Sergi JordàJun 2025This paper presents an overview of a human-machine collaborative musical performance by Raül Refree utilizing multiple MIDI-enabled pipe organs at Palau Güell, as part of the Organic concert series. Our earlier collaboration focused on live performances using drum generation systems, where generative models captured rhythmic transient structures while ignoring harmonic information. For the organ performance, we required a system capable of generating harmonic sequences in real-time, conditioned on Refree’s performance. Instead of developing a comprehensive state-of-the-art model, we integrated a more traditional generative method to convert our pitch-agnostic rhythmic patterns into harmonic sequences. This paper details the development process, the creative and technical considerations behind the final performance, and a reflection on the efficacy and adaptability of the chosen methodology.
2024
-
 Design, development, and deployment of real-time drum accompaniment systemsBehzad HakiDec 2024
Design, development, and deployment of real-time drum accompaniment systemsBehzad HakiDec 2024This dissertation examines the generation of real-time symbolic drum accompaniments, with a particular focus on live improvisation contexts. While the research does occasionally focus on the audio domain, the majority of the research is centered on symbolic-to-symbolic systems. This dissertation addresses real-time drum accompaniment from multiple perspectives: (1) conceptual, where a target application is designed based on a set of specified requirements, (2) architectural, where specific generative models are designed and developed for the selected conceptual design, and (3) deployment, where the conceptual design is realized and evaluated. Throughout this work, three accompaniment systems were developed and refined. The first work, detailed in Chapters 3 and 4, was aimed to develop a lightweight system on which future more sophisticated designs could be based. This system was based on a transformer model that was developed to convert a monotonic (single voice) rhythmic loop (groove) into a full multi-voice drum loop. The concept explored here was to investigate whether a loopbased system could be effectively used for generating drum accompaniments in long evolving improvisational sessions. The resulting system was evaluated by professional musician Raül Refree, who provided valuable insights on how the design could be modified to better suit the task. Following these evaluations, the second system, GrooveTransformer, was developed (discussed in Chapter 5). In this work, rather than relying on our personal speculations, we collaborated with Refree from the outset of the project. As such, we were able to develop a system that was far more suitable for the task at hand, to the extent that the musician felt comfortable to perform with the system in a public live improvisational session. While still loop-based, the generative model in this work was based on a variational transformer that enabled us to address the majority of the collaborating musician’s requirements for the system. Although initially deployed as software, we also developed a hardware Eurorack version (discussed in Chapter 6). The Eurorack module was designed to encourage experimentation and exploration beyond the system’s original intent. In the third system (discussed in Chapter 7), we moved beyond the loop-based approach. The primary goal was to enhance the system’s awareness of the evolving performance over extended durations. To this end, we developed a new generative model with a much larger context. The larger model’s computational demands required a thorough exploration of both conceptual and technical deployment strategies. All of these systems focused on converting a monotonic groove into a multivoice drum pattern. In Chapter 8, we first discuss the limitations and affordances of basing the generations solely on groove. Additionally, several works and proposals surrounding this groove-to-drum approach are discussed in detail: (1) how to improve the process of extracting grooves from polyphonic sources, (2) how to make this approach more accommodating for individuals with varying levels of musical experience, (3) how to expand the concept to generate general rhythms rather than exclusively drums, and (4) how to extract groove from audio sources. Beyond the primary objectives, this research also yielded several significant secondary contributions that arose from the explorations conducted. One such achievement was that we were able to establish that our systems can also be adapted to work with audios without major architectural changes (Appendix A). Moreover, we created NeuralMidiFx (Appendix B), a wrapper designed to facilitate the deployment of neural networks in VST (Virtual Studio Technology) format. This tool was developed to overcome the technical challenges encountered during the real-time deployment of the generative models. Furthermore, two novel datasets, TapTamDrum (Appendix C) and El Bongosero (Appendix D), were created as part of this research. These datasets serve as valuable resources for future studies on both rhythm generation and rhythm analysis.
-
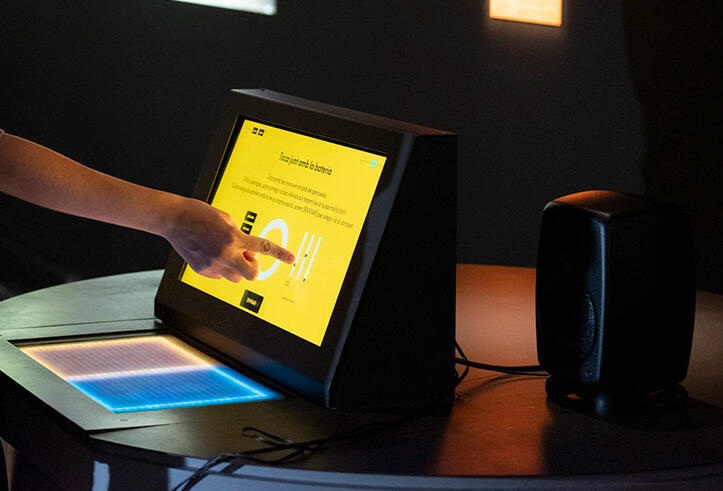 El Bongosero: A Crowd-sourced Symbolic Dataset of Improvised Hand Percussion Rhythms Paired with Drum PatternsNicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, Daniel Gomez, and 1 more authorNov 2024
El Bongosero: A Crowd-sourced Symbolic Dataset of Improvised Hand Percussion Rhythms Paired with Drum PatternsNicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, Daniel Gomez, and 1 more authorNov 2024We present El Bongosero, a large-scale, open-source symbolic dataset comprising expressive, improvised drum performances crowd-sourced from a pool of individuals with varying levels of musical expertise. Originating from an interactive installation hosted at Centre de Cultura Contemporània de Barcelona, our dataset consists of 6,035 unique tapped sequences performed by 3,184 participants. To our knowledge, this is the only symbolic dataset of its size and type that includes expressive timing and dynamics information as well as each participant’s level of expertise. These unique characteristics could prove to be valuable to future research, particularly in the areas of music generation and music education. Preliminary analysis, including a step-wise Jaccard similarity analysis on a subset of the data, demonstrate that this dataset is a diverse, nonrandom, and musically meaningful collection. To facilitate prompt exploration and understanding of the data, we have also prepared a dedicated website and an open-source API in order to interact with the data.
@inproceedings{Haki2024ELBNG, title = {{El Bongosero: A Crowd-sourced Symbolic Dataset of Improvised Hand Percussion Rhythms Paired with Drum Patterns}}, author = {Evans, Nicholas and Haki, Behzad and Gomez, Daniel and Jorda, Sergi}, booktitle = {{Proceedings of the 24th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference}}, year = {2024}, month = nov, publisher = {ISMIR}, } -
 Groove Transfer VST for Latin American RhythmsAnmol Mishra, Behzad Haki, Satyajeet Prabhu, and 1 more authorNov 2024
Groove Transfer VST for Latin American RhythmsAnmol Mishra, Behzad Haki, Satyajeet Prabhu, and 1 more authorNov 2024Latin American music relies on groove—small variations in timing, dynamics, and other aspects—to create an expressive rhythmic feel in music performance. Electronic music production often attempts to replicate these qualities through algorithmic manipulations to achieve similar effects. In this work, we employ a transformer-based model to learn microtiming and dynamics from onset timing and strength annotations of Uruguayan Candombe drum performances. The model is then deployed as a VST allowing users to apply the learnt candombe microrhythms to quantized midi drum performances. With this work, we aim to bridge the gap between algorithmic rhythm creation and the expressive qualities of live performance, striving to produce music with the authentic grooves of various Latin American genres.
@inproceedings{Mishra2024LBD, author = {Mishra, Anmol and Haki, Behzad and Prabhu, Satyajeet and Rocamora, Martín}, booktitle = {{the 25th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR)}}, year = {2024}, month = nov, publisher = {ISMIR}, title = {{Groove Transfer VST for Latin American Rhythms}}, } -
 GrooveTransformer: A Generative Drum Sequencer Eurorack ModuleNicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, and Sergi JordaSep 2024
GrooveTransformer: A Generative Drum Sequencer Eurorack ModuleNicholas Evans, Behzad Haki, and Sergi JordaSep 2024This paper presents the GrooveTransformer, a Eurorack module designed for generative drum sequencing. Central to its design is a Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE), around which we have designed a deployment context enabling performance through accompaniment and/or user interaction. This module allows the user to use the system as an accompaniment generator while interacting with the generative processes in real-time. In this paper, we review the design principles and technical architecture of the module, while also discussing the potentials and short-comings of our work.
@inproceedings{Haki2024GrooveTransformer, author = {Evans, Nicholas and Haki, Behzad and Jorda, Sergi}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression (NIME) 2024}, year = {2024}, month = sep, publisher = {NIME}, title = {{GrooveTransformer: A Generative Drum Sequencer Eurorack Module}}, }
2023
-
 TapTamDrum: A Dataset for Dualized Drum PatternsBehzad Haki, Błażej Kotowski, Cheuk Lee, and 1 more authorNov 2023
TapTamDrum: A Dataset for Dualized Drum PatternsBehzad Haki, Błażej Kotowski, Cheuk Lee, and 1 more authorNov 2023Drummers spend extensive time practicing rudiments to develop technique, speed, coordination, and phrasing. These rudiments are often practiced on "silent" practice pads using only the hands. Additionally, many percussive instruments across cultures are played exclusively with the hands. Building on these concepts and inspired by Einstein’s probably apocryphal quote, "Make everything as simple as possible, but not simpler," we hypothesize that a dual-voice reduction could serve as a natural and meaningful compressed representation of multi-voiced drum patterns. This representation would retain more information than its corresponding monotonic representation while maintaining relative simplicity for tasks such as rhythm analysis and generation. To validate this potential representation, we investigate whether experienced drummers can consistently represent and reproduce the rhythmic essence of a given drum pattern using only their two hands. We present TapTamDrum: a novel dataset of repeated dualizations from four experienced drummers, along with preliminary analysis and tools for further exploration of the data.
@inproceedings{Haki2023TapTamDrum, title = {{TapTamDrum: A Dataset for Dualized Drum Patterns}}, author = {Haki, Behzad and Kotowski, Błażej and Lee, Cheuk and Jorda, Sergi}, booktitle = {{Proceedings of the 24th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference}}, year = {2023}, month = nov, publisher = {ISMIR}, } -
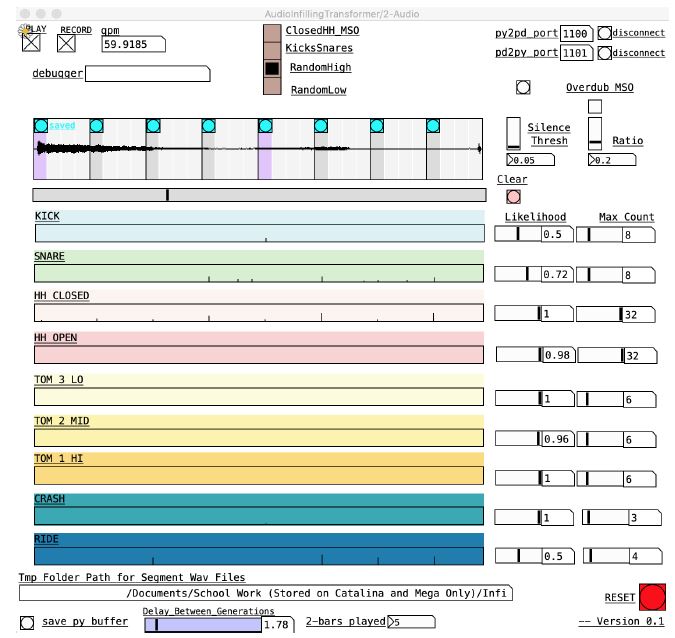
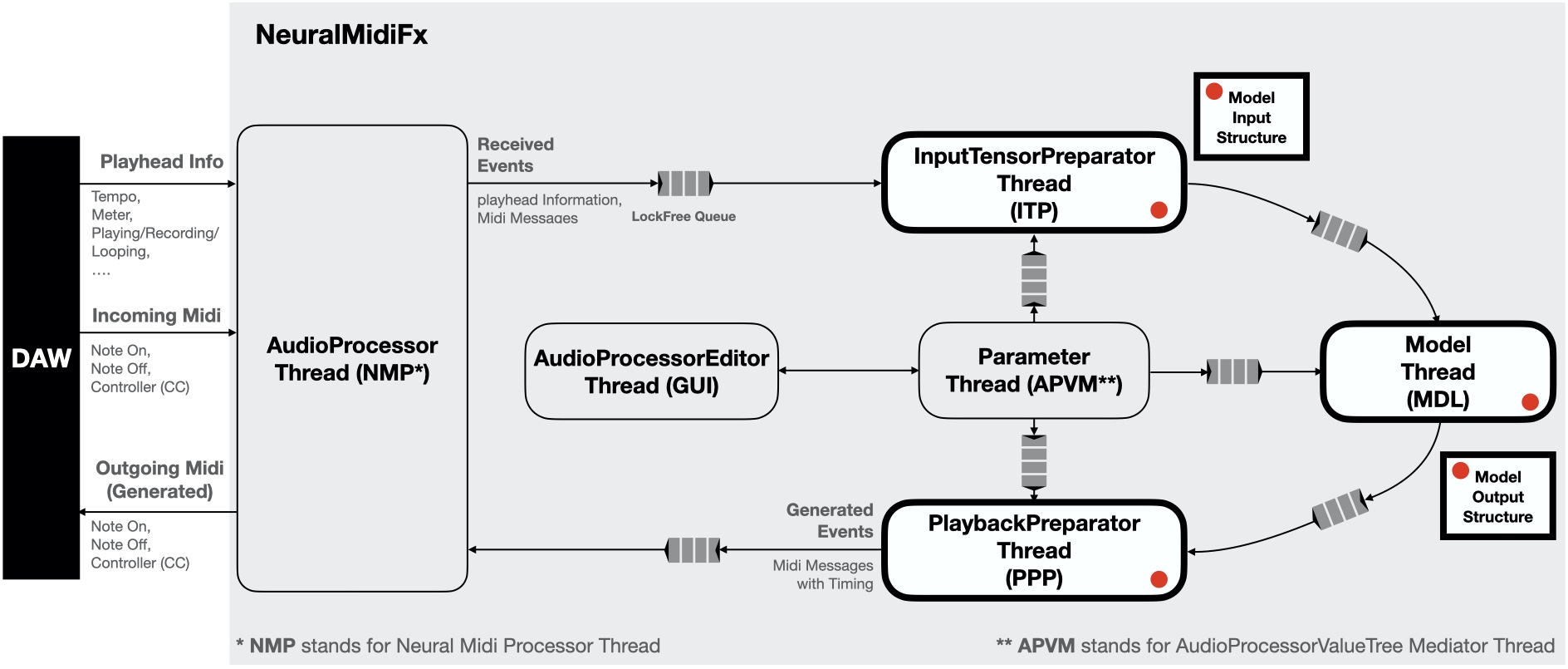 NeuralMidiFx: A Wrapper Template for Deploying Neural Networks as VST3 PluginsBehzad Haki, Julian Lenz, and Sergi JordaSep 2023
NeuralMidiFx: A Wrapper Template for Deploying Neural Networks as VST3 PluginsBehzad Haki, Julian Lenz, and Sergi JordaSep 2023Proper research, development and evaluation of AI-based generative systems of music that focus on performance or composition require active user-system interactions. To include a diverse group of users that can properly engage with a given system, researchers should provide easy access to their developed systems. Given that many users (i.e. musicians) are non-technical to the field of AI and the development frameworks involved, the researchers should aim to make their systems accessible within the environments commonly used in production/composition workflows (e.g. in the form of plugins hosted in digital audio workstations). Unfortunately, deploying generative systems in this manner is highly expensive. As such, researchers with limited resources are often unable to provide easy access to their works, and subsequently, are not able to properly evaluate and encourage active engagement with their systems. Facing these limitations, we have been working on a solution that allows for easy, effective and accessible deployment of generative systems. To this end, we propose a wrapper/template called NeuralMidiFx, which streamlines the deployment of neural network based symbolic music generation systems as VST3 plugins. The proposed wrapper is intended to allow researchers to develop plugins with ease while requiring minimal familiarity with plugin development.
@inproceedings{Haki2023NeuralMidiFx, author = {Haki, Behzad and Lenz, Julian and Jorda, Sergi}, booktitle = {{Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on on AI and Musical Creativity}}, publisher = {}, title = {{NeuralMidiFx: A Wrapper Template for Deploying Neural Networks as VST3 Plugins}}, year = {2023}, month = sep, } - Completing Audio Drum Loops with Symbolic Drum SuggestionsBehzad Haki, Teresa Pelinski, Marina Nieto, and 1 more authorApr 2023
Sampled drums can be used as an affordable way of creating human-like drum tracks, or perhaps more interestingly, can be used as a mean of experimentation with rhythm and groove. Similarly, AI-based drum generation tools can focus on creating human-like drum patterns, or alternatively, focus on providing producers/musicians with means of experimentation with rhythm. In this work, we aimed to explore the latter approach. To this end, we present a suite of Transformer-based models aimed at completing audio drum loops with stylistically consistent symbolic drum events. Our proposed models rely on a reduced spectral representation of the drum loop, striking a balance between a raw audio recording and an exact symbolic transcription. Using a number of objective evaluations, we explore the validity of our approach and identify several challenges that need to be further studied in future iterations of this work. Lastly, we provide a real-time VST plugin that allows musicians/producers to utilize the models in real-time production settings.
@inproceedings{Haki2023Completing, author = {Haki, Behzad and Pelinski, Teresa and Nieto, Marina and Jorda, Sergi}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression (NIME) 2023}, year = {2023}, month = apr, publisher = {NIME}, title = {{Completing Audio Drum Loops with Symbolic Drum Suggestions}}, }
2022
-
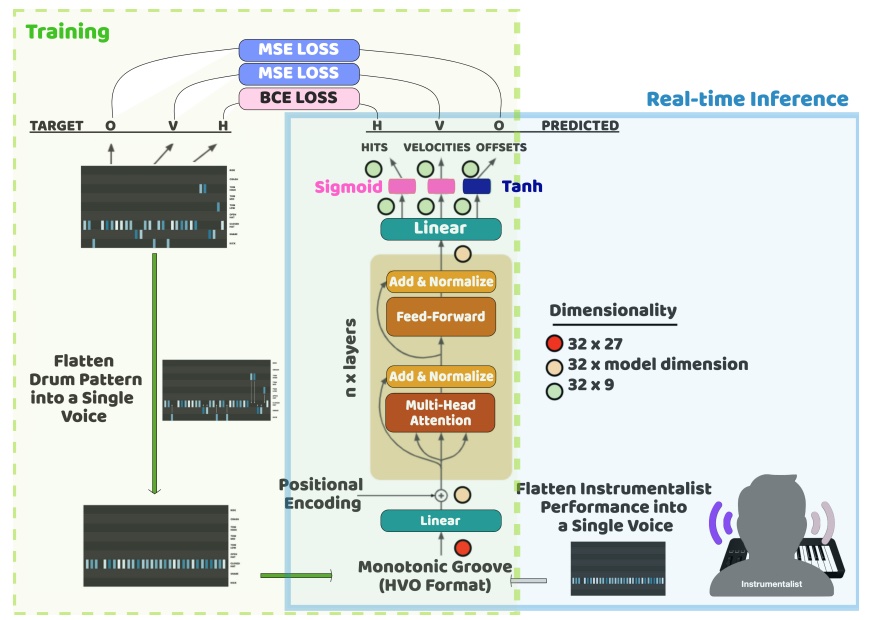 Real-Time Drum Accompaniment Using Transformer ArchitectureBehzad Haki, Marina Nieto, Teresa Pelinski, and 1 more authorSep 2022
Real-Time Drum Accompaniment Using Transformer ArchitectureBehzad Haki, Marina Nieto, Teresa Pelinski, and 1 more authorSep 2022This paper presents a real-time drum generation system capable of accompanying a human instrumentalist. The drum generation model is a transformer encoder trained to predict a short drum pattern given a reduced rhythmic representation. We demonstrate that with certain design considerations, the short drum pattern generator can be used as a real-time accompaniment in musical sessions lasting much longer than the duration of the training samples. A discussion on the potentials, limitations and possible future continuations of this work is provided.
@inproceedings{haki_behzad_2022_7088343, author = {Haki, Behzad and Nieto, Marina and Pelinski, Teresa and Jordà, Sergi}, title = {{Real-Time Drum Accompaniment Using Transformer Architecture}}, booktitle = {{Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on on AI and Musical Creativity}}, year = {2022}, publisher = {AIMC}, month = sep, doi = {10.5281/zenodo.7088343}, url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7088343}, }
2021
-
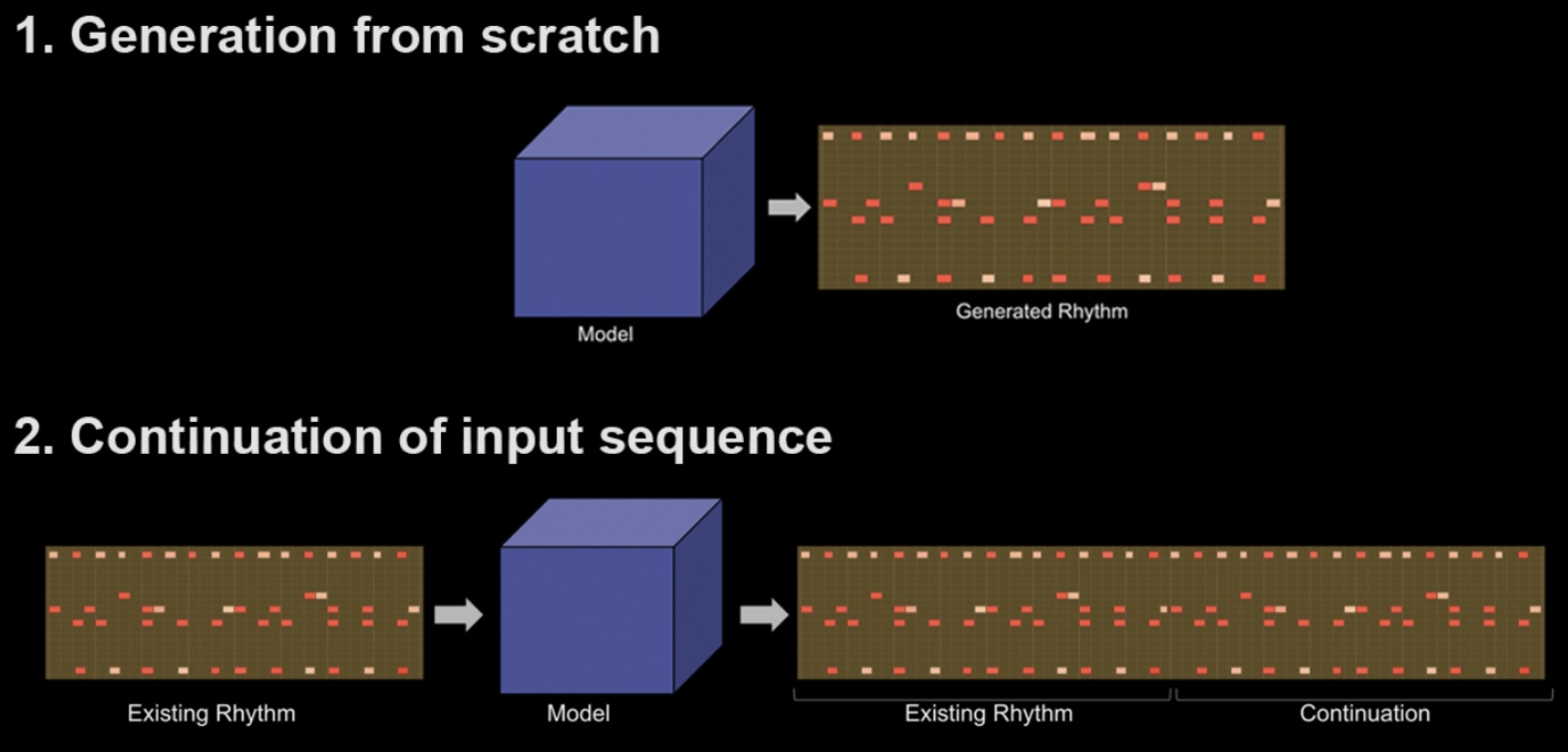 Transformer Neural Networks for Automated Rhythm GenerationThomas Nuttall, Behzad Haki, and Sergi JordaJun 2021
Transformer Neural Networks for Automated Rhythm GenerationThomas Nuttall, Behzad Haki, and Sergi JordaJun 2021Recent applications of Transformer neural networks in the field of music have demonstrated their ability to effectively capture and emulate long-term dependencies characteristic of human notions of musicality and creative merit. We propose a novel approach to automated symbolic rhythm generation, where a Transformer-XL model trained on the Magenta Groove MIDI Dataset is used for the tasks of sequence generation and continuation. Hundreds of generations are evaluated using blind-listening tests to determine the extent to which the aspects of rhythm we understand to be valuable are learnt and reproduced. Our model is able to achieve a standard of rhythmic production comparable to human playing across arbitrarily long time periods and multiple playing styles.
@inproceedings{NIME21_33, article-number = {33}, author = {Nuttall, Thomas and Haki, Behzad and Jorda, Sergi}, title = {Transformer Neural Networks for Automated Rhythm Generation}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression}, year = {2021}, month = jun, address = {Shanghai, China}, issn = {2220-4806}, doi = {10.21428/92fbeb44.fe9a0d82}, url = {https://nime.pubpub.org/pub/8947fhly}, presentation-video = {https://youtu.be/Ul9s8qSMUgU}, }
2019
-
 A Bassline Generation System Based on Sequence-to-Sequence LearningBehzad Haki, and Sergi JordaJun 2019
A Bassline Generation System Based on Sequence-to-Sequence LearningBehzad Haki, and Sergi JordaJun 2019This paper presents a detailed explanation of a system generating basslines that are stylistically and rhythmically interlocked with a provided audio drum loop. The proposed system is based on a natural language processing technique: word-based sequence-to-sequence learning using LSTM units. The novelty of the proposed method lies in the fact that the system is not reliant on a voice-by-voice transcription of drums; instead, in this method, a drum representation is used as an input sequence from which a translated bassline is obtained at the output. The drum representation consists of fixed size sequences of onsets detected from a 2-bar audio drum loop in eight different frequency bands. The basslines generated by this method consist of pitched notes with different duration. The proposed system was trained on two distinct datasets compiled for this project by the authors. Each dataset contains a variety of 2-bar drum loops with annotated basslines from two different styles of dance music: House and Soca. A listening experiment designed based on the system revealed that the proposed system is capable of generating basslines that are interesting and are well rhythmically interlocked with the drum loops from which they were generated.
@inproceedings{haki2019, author = {Haki, Behzad and Jorda, Sergi}, title = {A Bassline Generation System Based on Sequence-to-Sequence Learning}, pages = {204--209}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on New Interfaces for Musical Expression}, editor = {Queiroz, Marcelo and Sedó, Anna Xambó}, year = {2019}, month = jun, publisher = {UFRGS}, address = {Porto Alegre, Brazil}, issn = {2220-4806}, doi = {10.5281/zenodo.3672928}, }